Prevention plan: the simple and effective method to ensure the company's safety
Published on February 14, 2025
Prevention plan: the simple and effective method to ensure the company's safety


With the Prevention Plan template (in French only), collectively identify the risks and determine the measures to adopt to ensure safety within your organization.
Create your prevention plan simply and in one place
Are you carrying out work in your organization? Guarantee safety and manage risks by drawing up a prevention plan. With the Prevention Plan Template, you can easily mobilize all stakeholders to identify risks and adopt the appropriate measures, in a collective and visual way.
Risk prevention is a key element in the security of organizations and is a subject that should not be taken lightly. What is the prevention plan, what is it used for and in which cases must it be drawn up? What are the obligations related to the Labor Code? Who is in charge of the realization of the plan and who signs it in fine? How to elaborate from A to Z and update the prevention plan? Answers below.
A prevention plan is a document produced by a group of actors aiming at preventing the risks of co-activity when a company intervenes in the premises of another company (maintenance operations, renovation, etc.). A prevention plan is mandatory when the duration of the work is at least 400 hours over 12 months and if the work is considered as dangerous, whatever the duration (decree of 20 February 1992).
The prevention plan must contain at least the following information:
The prevention plan is valid:
Each company keeps a copy of the prevention plan. If the outside company uses subcontractors, it must send them the prevention plan so that they can apply the prevention measures. The prevention plan must also be made available to the work inspector, the CARSAT (retirement insurance fund), the OPPBTP (Professional Prevention Organization for Construction and Public Works), the work doctor and the staff representatives.
With Klaxoon and the template available above, you will be able to develop your prevention plan in a fluid manner by mobilizing stakeholders throughout the process. The Meeting activity, a Klaxoon presentation tool, combined with Board (Klaxoon's digital whiteboard) makes it possible to meet these regulatory obligations. As the backbone of the plan, the Meeting allows to connect all the stakeholders and to animate in the form of workshops the 2 main sequences: the common preliminary inspection and the realization of the plan. Thanks to the complete report in PDF format generated automatically at the end of the plan, all the steps can be traced and this report is authentic with the control actors. It can also be stored and distributed.
The establishment of a prevention plan is at the initiative of the company in which the work takes place, called the "user company". The prevention plan must be drawn up jointly by the manager of the company carrying out the work (known as the "external company") and the manager of the user company.
With the Prevention Plan template, the user company, through its safety manager or another player responsible for implementing the plan, can launch the project, monitor it from A to Z and manage the various stages with one tool, in one place. All the stakeholders can be integrated into the process simply by sharing Klaxoon activities via a link or a code. Everyone will be able to participate in the pre-inspection, plan completion and update stages. Using Klaxoon, the prevention plan links analysis and operational reality.
The prevention plan is built through 2 main phases, which can be facilitated during workshops with stakeholders.
The joint pre-inspection
Before drawing up this risk prevention plan, the company managers or their representatives must carry out a prior joint inspection. The purpose of this inspection is to get to know the work site, to analyze the risks related to the co-activity, the installations and the materials, and to plan the necessary prevention measures to avoid any dangerous event occurring.
How do you conduct the joint pre-inspection using Klaxoon?
Prior to the visit, the safety manager in charge of the prevention plan creates a Meeting and a Board in a very simple way, by following the steps indicated in the Prevention Plan template. All he has to do is to invite the participants, via a code or a simple web link. On their computer or smartphone prior to the visit, each participant completes a Survey that allows the facilitator to collect information on the representatives of the stakeholders and the details of the planned operations.
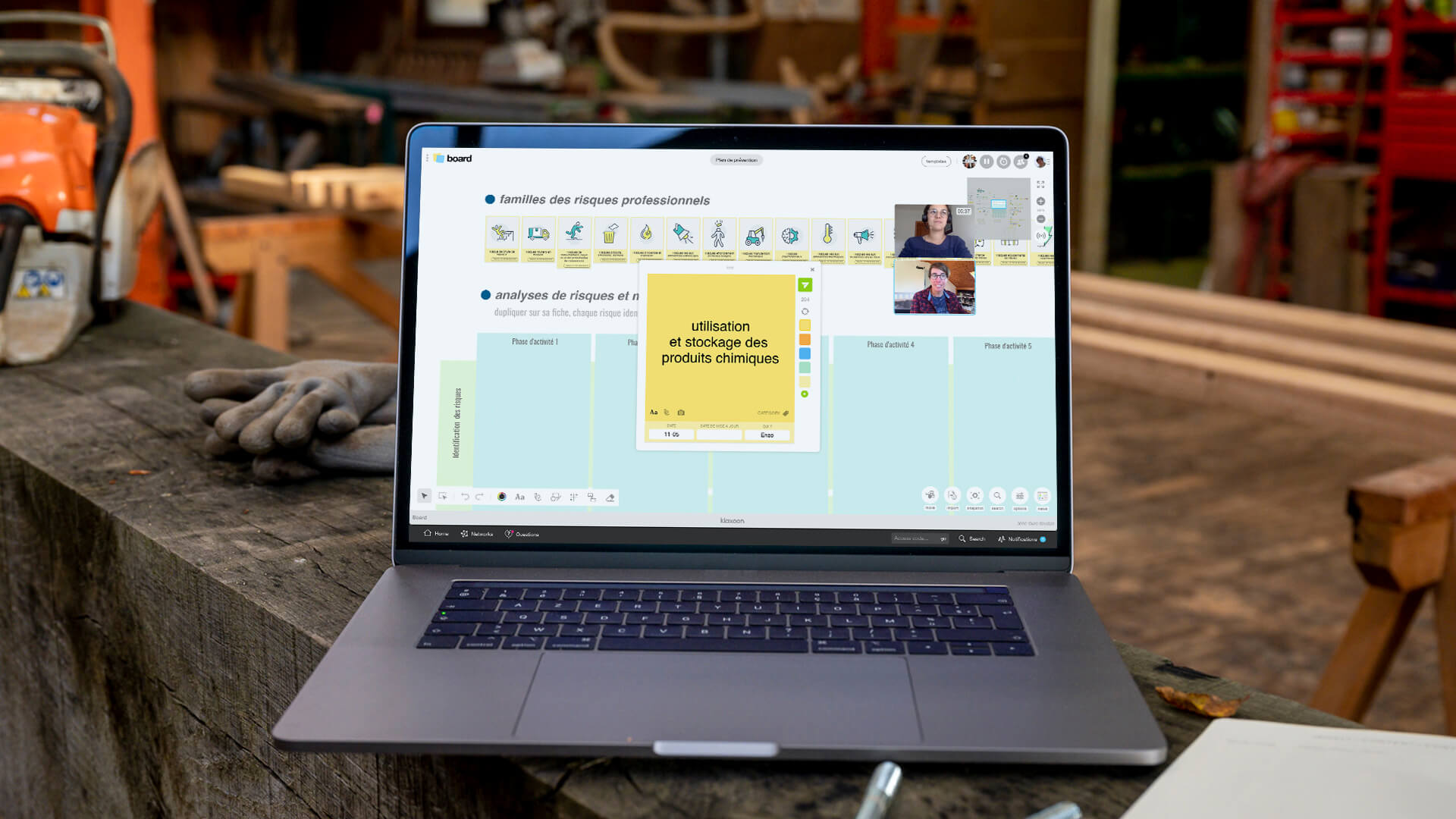
Then, the Board evolves throughout the joint preliminary inspection. The Board is a collaborative digital whiteboard, with infinite space, on which everyone can share any type of idea using the codes of visual management. Everyone feeds it in a very simple way: by taking pictures with their smartphone and posting them in the zones provided for this purpose. All potential risks are thus listed and visible in the same place. Once the visit is completed, the facilitator uses the answers to the Survey and the photos to define the activity phases whose risks will have to be analyzed. An area of the Board is also dedicated to the documents that will have to be transmitted by the facilitator according to the planned interventions. For example, the necessary collective protective equipment, safety instructions or product technical notices. The trainer can use Questions to transmit these documents to the concerned persons with the adapted format during or after the workshop. The Questions tool makes it easy to ask each other to elaborate on a topic, or to get feedback.
After a regulatory period of at least 3 days following the joint preliminary inspection, the risk analysis can take place, which launches the plan implementation phase. The risk analysis must follow a certain number of principles codified in the legislative part of the labor code. Like all occupational risk analyses, it must comply with the following general prevention principles (defined in article L.4121-1):
In addition to these prevention principles, it should be remembered that the prevention plan consists of choosing methods, materials and procedures that avoid interference with the risks identified by the activity of each company.
How to conduct a risk analysis with Klaxoon?
This time takes place synchronously, during a second workshop led by the safety manager: everyone is connected to the Meeting and accesses the Prevention Plan Board again. The facilitator uses the Board Synchro: this feature allows to focus on one area of the Board so that each participant sees the same space on his screen, at the same time. The facilitator first invites participants to complete the dedicated area with their photo and contact information. The group then scans the risk families on which the analysis is based. The activity phases identified by the facilitator through the survey are reviewed: phase after phase, the group expresses itself on the risks it identifies very simply, by posting ideas. A like phase can take place to decide which main risks are to be taken into account. That is to say that everyone gives a small heart to the idea for which they vote. The selected risks are selected and reported in the dedicated area.
Once the risks have been identified, the stakeholders are invited to reflect on the measures to be adopted to avoid the occurrence of dangerous events. These measures revolve around protective equipment, safety instructions and the necessary worker authorizations and training.
Collective protective equipment or CPE is intended to limit or confine and is always implemented in priority to Personal Protective Equipment. For example, if during the preliminary inspection a work situation is identified where there is a risk of a person falling, it will be necessary to determine the measures to be adopted to avoid this situation. In particular, the employer will have to take the following measures:
Personal protective equipment (or PPE) are devices or means intended to be worn or held by a person in order to protect him or her against one or more risks likely to threaten his or her health and safety (articles R. 4311-12 to R. 4311-14 modified of the French Labor Code). For example, a helmet, safety shoes, glasses, respiratory protection masks, earplugs, gloves, protective clothing, etc. Personal protection should only be considered when all other measures to eliminate or reduce the risk are insufficient or impossible to implement. The head of the establishment must make them available to exposed employees when the situation justifies it.
Safety instructions describe the procedures to be followed in case of a dangerous event or an accident for example. Giving the alert, making safe, monitoring... All the information relating to these actions must be communicated before the planned interventions.
The training in gestures and postures or the electrical authorizations are elements often requested and necessary in the implementation of these operations and essential to ensure the quality of the participants in their personal and collective safety. For example, if the work involves the preparation, use, handling or exposure to certain agents.
These measures can be indicated directly in the Board and specified through web links, regulatory documents, etc. The facilitator reports the measures selected for each risk: the group can see at a glance the main risks and the measures to be adopted for all the planned activity phases. The facilitator uses the capture tool to determine the risks and measures selected: these elements are automatically added to the Meeting and will appear in the PDF report at the end of the plan.
To conclude this phase of the plan, the stakeholders sign directly in the Board: they just have to post their picture and sign in an idea with name and date. If needed, the signing authority can be added by the stakeholder in a Question, the facilitator can then record the document. The facilitator captures all signatures and each step of the prevention plan to complete the minutes. The Board is completed and the Meeting can be closed so that the PDF report is automatically generated.
Company directors or safety managers produce an average of 40 prevention plans per year. These prevention plans must be updated at least every quarter. In addition, during maintenance or work operations, joint inspections may reveal unanticipated risks. In this case, an update of the prevention plan is necessary.
To update the prevention plan, the facilitator simply reopens the Meeting and clicks on the Board to access it and make the changes. It is also possible to duplicate the Board to keep the initial results. To store all the prevention plans, access them with one click and update them, the facilitator can group them in a Network. A Network allows you to group together several activities related to the same project, to be shared with a group of people dedicated to this project. Only the group of people subscribed to the Network will have access to the activities it contains.
Create your prevention plan with this Klaxoon template, in a participative and fluid way!

Get inspired by other templates from the same categories
Unlock your teamwork potential